Mekong Delta history of formation and development
- Fri, 26/07/2019
- 11161 viewed
- 0 commented
The Mekong Delta region consists of 12 provinces in total: Long An, Tien Giang, Ben Tre, Vinh Long, Tra Vinh, Soc Trang, Dong Thap, An Giang, Hau Giang, Kien Giang, Bac Lieu and Ca Mau and 1 central city is Can Tho City.
The typical peaceful landscape of the countryside in Vietnam along with the ardent and honest people both have created a distinctive characteristic of the Mekong Delta. Now let’s go with Viet Fun Travel to explore more about Mekong Delta history which absolutely intrigued you.
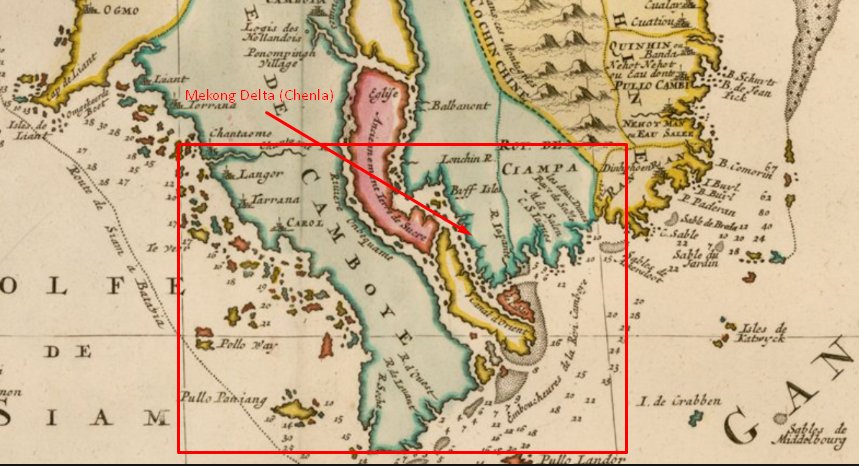
Mekong Delta Map in The 18th century
Formed from alluvial sediments and accreted over the changing era of sea level, the Southwest region is also known as the largest granary of Vietnam, currently being one of 7 major Vietnam's economic regions.
In 1698 Nguyen Huu Canh was sent by Lord Nguyen Phuc Chu to establish Vietnamese administrative structures in the area of Chenla land. He divided Dong Pho land of Chinese people into districts and then governed. Nguyen Lord again recruited people from Quang Binh which is located in the middle of Vietnam to come back to set up villages and communes, and the Vietnamese and Chinese people here were under the government of Nguyen Lord and Viet nation.
Mac Cuu is a native of Guangdong, but because Qing Dynasty toppled the Ming Dynasty from the throne, so he and his family moved to Chenla. In 1680, Mac Cuu expanded his land to include the lands of Ha Tien, Rach Gia and Phu Quoc, which belonged to Chenla but the control of the Chenla court couldn’t reach.
Till 1757, Nguyen lord possessed many lands of Chenla, which are the West of Vietnam now.
King Minh Mang in 1832 set out in Cochinchina (Nam Ky) and divided it into 6 provinces, so it was called Nam Ky Luc Tinh or also known as Luc Tinh.
In 1836, the king changed Gia Dinh (Saigon city) to Bien Hoa (Bien Hoa province) Dinh Tuong (My Tho city) in the East and Vinh Long (Vinh Long province) An Giang (Chau Doc city) Ha Tien (Ha Tien province) in the West.
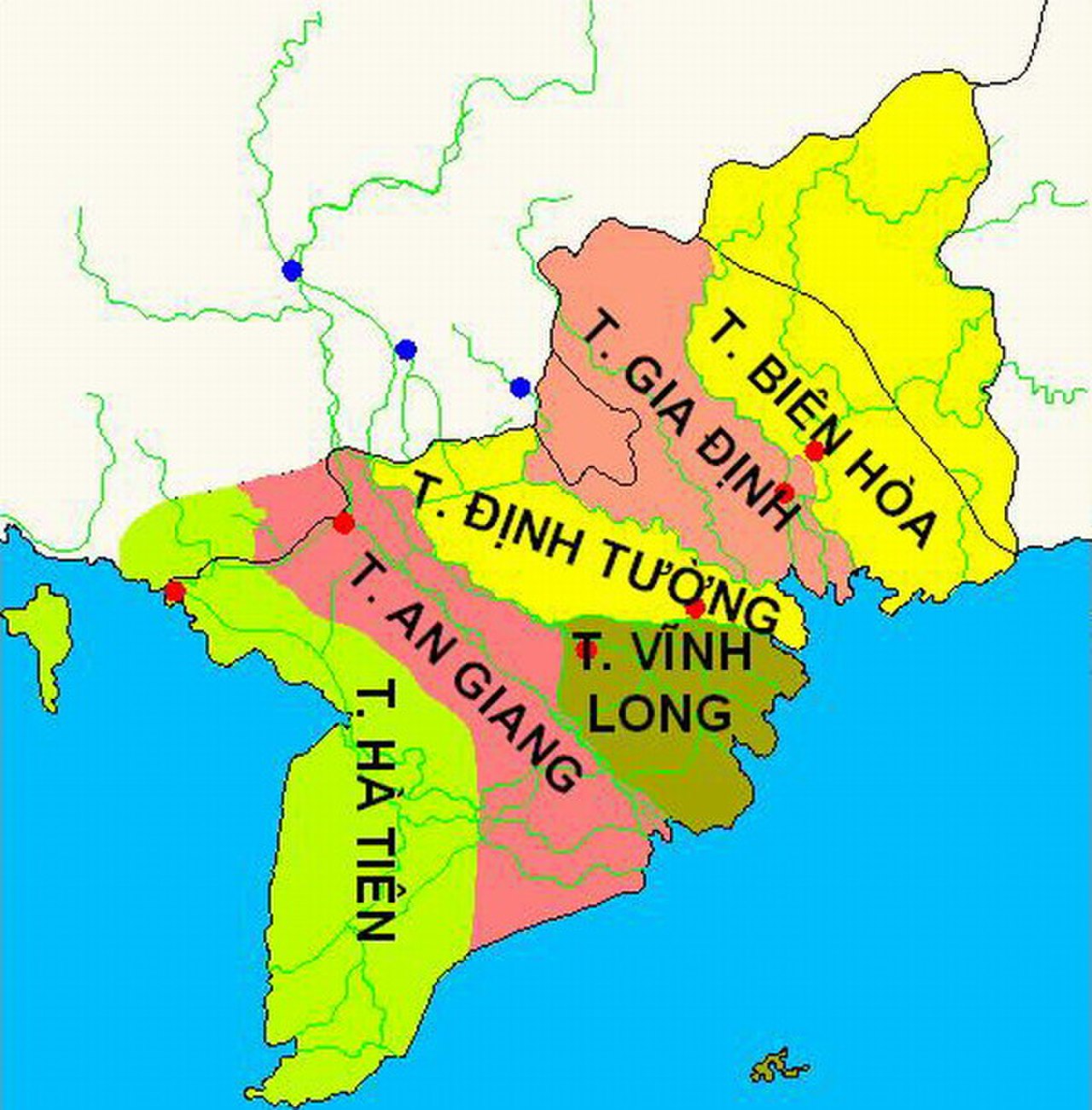
Among the 6 provinces in Cochinchina at that time, there were 4 provinces in the Southwest region (Mekong Delta) including: Dinh Tuong, Vinh Long, An Giang and Ha Tien.
There is also a part of Gia Dinh province at that time in the Southwest region, equivalent to a part of Long An and Tien Giang provinces (Go Cong land) today.
Thus, till 1845, neighboring countries with Vietnam, including Cambodia, signed official legal documents and recognized the Southern region of Vietnam.
In 1858, the French attacked South Vietnam and in turn occupied 6 Nam Ky provinces, the Nguyen Dynasty mobilized the army to conduct resistance against the French. When the resistance failed, the Nguyen court signed concessions to France 3 Eastern provinces (in 1862) and 3 western provinces (in 1874).
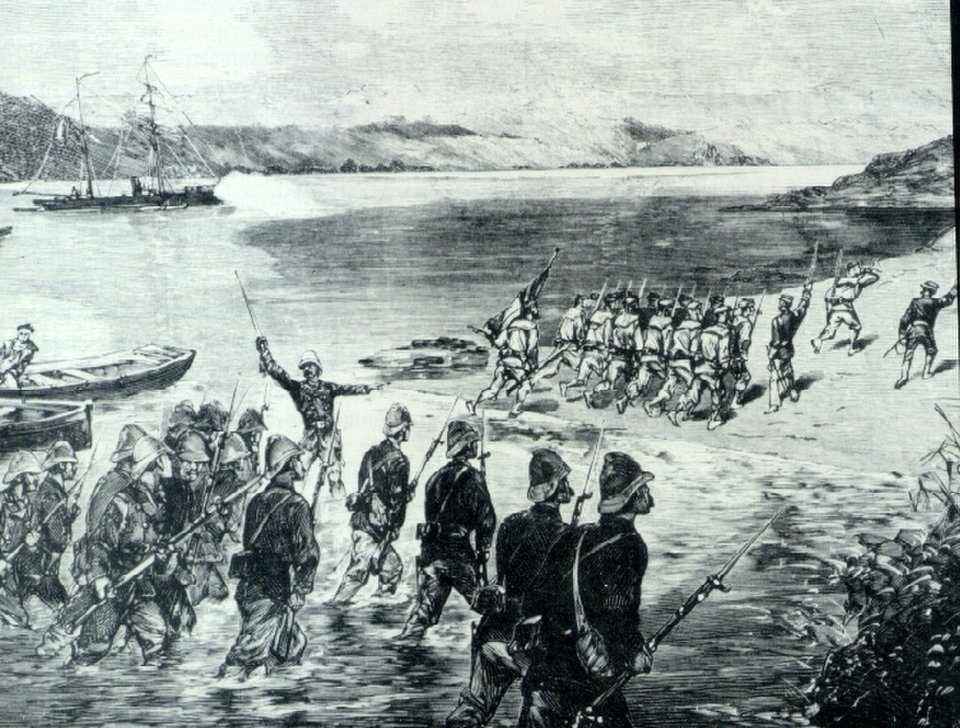

The France invaded Mekong Delta in 1858
After establishing the Indochina Federation, France exercised sovereignty over the land of Southern Vietnam, carried out border planning between South Vietnam and Cambodia under French law. In 1889, France and Cambodia signed a series of legal documents to plan and demarcate the border between Nam Ky and Cambodia.
On June 4, 1949, due to the success of Vietnam in the war against France, the French President V. Auriol signed the Code No. 49-733 to return Nam Ky to the Bao Dai government.
Thus, in 1949, the land of Nam Bo, which had been "ceded" by the Nguyen Dynasty to the French colonialists was returned to Vietnam with a legal document, the French Government affirmed its historical bases and the law of this document with the Kingdom of Cambodia.
Since then, the sovereignty of Vietnam on the land of Southern Vietnam has been recognized by international legal agreements as the Agreement of Gieneve (1954) between Vietnam and France; The Paris Agreement (1973) between Vietnam and the US, is recognized by the international community including Laos and Cambodia.
During the 21 years of resistance war against the US, the country was divided, there were many conflicts of sovereignty disputes between the government of Saigon and Cambodia. On May 9, 1967, the Kingdom of Cambodia issued a statement calling on countries to respect the territorial integrity of Cambodia in its current border.
Facing that situation, on May 31, 1967 and June 8, 1967, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam Government issued a statement recognizing and respecting Cambodia's current border.
And by the end of 1968, 34 countries around the world had declared Cambodia's respect for the sovereignty of territorial integrity in the current border.
Since the reunification of the country (April 30, 1975), the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and Cambodia have signed treaties:
- The peace, friendship and cooperation agreement between the two countries was signed on February 18, 1979.
- The land border treaty signed on July 20, 1983.
- National border planning agreement between the two countries signed on December 27, 1985.
- Agreement to supplement the Border Planning Treaty in 1985, signed on October 10, 2005 between the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and the Government of the Kingdom of Cambodia.

Can Tho city in 1975
On September 7, 2006, representatives of the governments of the two countries began to build the first international milestone at Moc Bai border gate (Tay Ninh Vietnam) and Ba Vet (Cambodia), and in early 2008, completed road landmarks which are the land border between Vietnam and Cambodia.
Above are the important events demonstrating how the Mekong Delta region was established over many different historic periods. We hope that through this article, it will help you to gain a thorough insight about Mekong Delta history. If you have any question, please don’t hesitate to comment below, we will contact you as soon as possible.
The typical peaceful landscape of the countryside in Vietnam along with the ardent and honest people both have created a distinctive characteristic of the Mekong Delta. Now let’s go with Viet Fun Travel to explore more about Mekong Delta history which absolutely intrigued you.

Mekong Delta Map in The 18th century
Overview of the Mekong Delta region
Mekong Delta or often called Southwest region is part of the delta of the Mekong River with an area of 40.6 thousand km2, occupying an area of about 12.3% of the area of the whole country and the coastal area extending up to 700km, thus creating favorable conditions for the development of the marine economy.Formed from alluvial sediments and accreted over the changing era of sea level, the Southwest region is also known as the largest granary of Vietnam, currently being one of 7 major Vietnam's economic regions.
The Mekong Delta history over the course of time
Mekong Delta was in the past the territory of Funan and later Chenla and shared the formation process.Nguyen and Tay Son lords
In 1658, Lord Nguyen Phuc Tan helped the royal relative of Chenla, Batom Reachea, to the throne and signed a treaty with Chenla court to allow Vietnamese to own the land reclaimed in Saigon, Dong Nai and Ba Ria.In 1698 Nguyen Huu Canh was sent by Lord Nguyen Phuc Chu to establish Vietnamese administrative structures in the area of Chenla land. He divided Dong Pho land of Chinese people into districts and then governed. Nguyen Lord again recruited people from Quang Binh which is located in the middle of Vietnam to come back to set up villages and communes, and the Vietnamese and Chinese people here were under the government of Nguyen Lord and Viet nation.
Mac Cuu is a native of Guangdong, but because Qing Dynasty toppled the Ming Dynasty from the throne, so he and his family moved to Chenla. In 1680, Mac Cuu expanded his land to include the lands of Ha Tien, Rach Gia and Phu Quoc, which belonged to Chenla but the control of the Chenla court couldn’t reach.
Till 1757, Nguyen lord possessed many lands of Chenla, which are the West of Vietnam now.
Nguyen Dynasty
During the Nguyen Dynasty founded in 1802, King Gia Long continued the career of Nguyen lords, completed the administrative system and unified management on a national scale.King Minh Mang in 1832 set out in Cochinchina (Nam Ky) and divided it into 6 provinces, so it was called Nam Ky Luc Tinh or also known as Luc Tinh.
In 1836, the king changed Gia Dinh (Saigon city) to Bien Hoa (Bien Hoa province) Dinh Tuong (My Tho city) in the East and Vinh Long (Vinh Long province) An Giang (Chau Doc city) Ha Tien (Ha Tien province) in the West.

Among the 6 provinces in Cochinchina at that time, there were 4 provinces in the Southwest region (Mekong Delta) including: Dinh Tuong, Vinh Long, An Giang and Ha Tien.
There is also a part of Gia Dinh province at that time in the Southwest region, equivalent to a part of Long An and Tien Giang provinces (Go Cong land) today.
During the resistance war against France and America
In December 1845, three countries of An Nam (Vietnam), Siam (Thailand) and Mien (Cambodia) signed a treaty, acknowledging 6 Southern provinces of Vietnam. The year after 1846, the Nguyen and Siam dynasties signed another treaty that repeated that. This is a treaty that later on, Cao Mien also participated.Thus, till 1845, neighboring countries with Vietnam, including Cambodia, signed official legal documents and recognized the Southern region of Vietnam.
In 1858, the French attacked South Vietnam and in turn occupied 6 Nam Ky provinces, the Nguyen Dynasty mobilized the army to conduct resistance against the French. When the resistance failed, the Nguyen court signed concessions to France 3 Eastern provinces (in 1862) and 3 western provinces (in 1874).

The France invaded Mekong Delta in 1858
After establishing the Indochina Federation, France exercised sovereignty over the land of Southern Vietnam, carried out border planning between South Vietnam and Cambodia under French law. In 1889, France and Cambodia signed a series of legal documents to plan and demarcate the border between Nam Ky and Cambodia.
On June 4, 1949, due to the success of Vietnam in the war against France, the French President V. Auriol signed the Code No. 49-733 to return Nam Ky to the Bao Dai government.
Thus, in 1949, the land of Nam Bo, which had been "ceded" by the Nguyen Dynasty to the French colonialists was returned to Vietnam with a legal document, the French Government affirmed its historical bases and the law of this document with the Kingdom of Cambodia.
Since then, the sovereignty of Vietnam on the land of Southern Vietnam has been recognized by international legal agreements as the Agreement of Gieneve (1954) between Vietnam and France; The Paris Agreement (1973) between Vietnam and the US, is recognized by the international community including Laos and Cambodia.
During the 21 years of resistance war against the US, the country was divided, there were many conflicts of sovereignty disputes between the government of Saigon and Cambodia. On May 9, 1967, the Kingdom of Cambodia issued a statement calling on countries to respect the territorial integrity of Cambodia in its current border.
Facing that situation, on May 31, 1967 and June 8, 1967, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam Government issued a statement recognizing and respecting Cambodia's current border.
And by the end of 1968, 34 countries around the world had declared Cambodia's respect for the sovereignty of territorial integrity in the current border.
Since the reunification of the country (April 30, 1975), the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and Cambodia have signed treaties:
- The peace, friendship and cooperation agreement between the two countries was signed on February 18, 1979.
- The land border treaty signed on July 20, 1983.
- National border planning agreement between the two countries signed on December 27, 1985.
- Agreement to supplement the Border Planning Treaty in 1985, signed on October 10, 2005 between the Government of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and the Government of the Kingdom of Cambodia.

Can Tho city in 1975
On September 7, 2006, representatives of the governments of the two countries began to build the first international milestone at Moc Bai border gate (Tay Ninh Vietnam) and Ba Vet (Cambodia), and in early 2008, completed road landmarks which are the land border between Vietnam and Cambodia.
Above are the important events demonstrating how the Mekong Delta region was established over many different historic periods. We hope that through this article, it will help you to gain a thorough insight about Mekong Delta history. If you have any question, please don’t hesitate to comment below, we will contact you as soon as possible.
Comment
Name:
Email:
Enter code confirmation number inside under:

Your comments:
Send
Other news
- Xeo Quyt Relic Area: A unique charm of Mekong Delta
- A List of Top Pagodas and Temples in Dong Thap
- Things to know about Can Tho Floating Market & Wildlife
- Can Tho Night Market – Best Nightlife Activity
- Travel to Mekong Delta or Hoi An. Where one should you choose?
- How to get from Mekong Delta to Phnom Penh?
- Tram chim national park Dong Thap- a wonderland of Mekong Delta
- Mekong Delta Homestay – A hands-on and interesting experience
- Sa Dec Flower Village- a favorite tourist attraction for flower lovers
- Mekong Delta or Halong Bay: Which is more attracted…find out NOW
- The charm of Folk Music in Mekong Delta
- How to get from Ho Chi Minh city to Phu Quoc?
- Things to do in Ca Mau and The Best Time to Travel this place?
- Things to do in Tra Vinh – What you should not miss
- 5 Best Things to Do in Kien Giang - Top Attractions in Kien Giang
- Interesting things to do in Bac Lieu that you must try
- Things to do in Soc Trang Province– A Guide for Newbies
- Best Things to Do in Hau Giang - Top attraction
- Top 7 Things to Do in Dong Thap Province
- Top Best Things to Do in Long Xuyen City When you visit


 Shopping Cart
Shopping Cart Checkout
Checkout